BACKGROUND
This general information chapter is derived from the Certificate of Analysis Guide for Bulk Pharmaceutical Excipients, prepared by The International Pharmaceutical Excipients Council of the Americas (IPEC-Americas), an international guidance document on the preparation and appropriate use of a Certificate of Analysis (COA) for these excipients, referenced throughout the chapter as “excipient(s)”. The chapter defines the suggested elements of a Certificate of Analysis, provides a template for organizing required and optional data in a logical manner, and assists in establishing a uniform understanding of the roles and responsibilities of excipient manufacturers, distributors, and users.
The principles and information in this chapter can be applied to the manufacture of all bulk pharmaceutical excipients intended for use in human drugs, veterinary drugs, and biologics. As an international guidance document, it cannot specify all national legal requirements nor cover in detail the particular characteristics of every excipient. When considering how to use this chapter, each manufacturer, distributor, or user should consider how it may apply to that specific manufacturer's product and processes. The diversity of excipients means that some principles of the chapter may not be applicable to certain products and processes.
The chapter is divided into several parts. The first part provides background discussion necessary for the design and suggested elements of a COA. A template is provided to show the format and placement of information in the COA. This is followed by a detailed discussion to ensure that the purpose and meaning of the specific information contained in the COA is understood. For a list of terms used in this information chapter and their definitions, see Appendix 1.
GENERAL GUIDANCE
International regulations governing drugs require that components of the drugs be manufactured, processed, packed, and held in accordance with good manufacturing practices (GMPs). For a thorough discussion of GMPs that apply to excipient manufacture, see Good Manufacturing Practices for Bulk Pharmaceutical Excipients  1078
1078 . The excipient is often a natural substance, mixture, or polymer whose chemical and physical properties are difficult to quantify and that is often used with a broad range of active pharmaceutical ingredients and in a diverse range of finished dosage forms. Until now, there were no guidance documents that specifically focused on the content or format of COAs for excipients and that addressed the diversity of both the excipients and their usage.
. The excipient is often a natural substance, mixture, or polymer whose chemical and physical properties are difficult to quantify and that is often used with a broad range of active pharmaceutical ingredients and in a diverse range of finished dosage forms. Until now, there were no guidance documents that specifically focused on the content or format of COAs for excipients and that addressed the diversity of both the excipients and their usage.
Preparation and Appropriate Use of a Certificate of Analysis—
The Certificate of Analysis for excipients should be prepared and issued by the supplier of the material, following the general guidelines discussed below. Primary responsibility for the preparation of the COA belongs to the excipient manufacturer. It is most important that a complete and accurate COA be provided to the excipient user for specific lots or batches intended for use in the pharmaceutical industry. Additional considerations should be made for the preparation and issuance of a COA by a distributor of excipients.
The user of a bulk pharmaceutical excipient should always receive a COA for material to be used in the manufacture of a drug product. At a minimum, the user should perform adequate identification tests on each lot of excipient received before releasing it for use in the drug product. Specific identity tests should be used whenever possible. It is a regulatory requirement that excipients be assessed for conformity with all appropriate specifications. However, testing of all specification parameters may not be required for lot release if adequate compliance assurances are provided on the supplier's COA. Before using an excipient in a pharmaceutical product based on COA data, the user also should have an understanding of the supplier's control systems and compliance with GMPs, through appropriate auditing or qualification of the supplier.
Nevertheless, it is the responsibility of the user of the excipient to verify any of the analytical data contained in the COA if knowledge of such information is deemed essential to the use of that excipient. Such testing may go beyond the scope of the compendial methods described in the NF, or beyond those used to develop the information in the COA.
To use test results from a COA, the user must also establish the reliability of the supplier's COA test results by periodically performing all required tests and comparing the results obtained to the supplier's test results. Occasionally, it may not be possible to perform all the required tests because of special equipment requirements, etc., that may not be available to the user. Performing fewer than all these tests may be acceptable provided that the reliability of the supplier has been adequately determined using other appropriate supplier qualification techniques.
It is important to understand that these results may not always specifically correlate, especially when an excipient is produced as a continuous lot. However, the user's test results should demonstrate compliance with the specification requirement.
Use of Contract Facilities—
Contract facilities are frequently used in the manufacture, testing, and distribution of excipients. When such facilities are used, the supplier of the excipient has the obligation to ensure that the facilities operate under appropriate quality standards (i.e., cGMP, GLP, etc.).
DESIGN AND SUGGESTED ELEMENTS OF A CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS
The suggested elements of a COA are listed below and are included in the following Certificate of Analysis Template section of this chapter. Excipient suppliers may organize the suggested elements presented in the COA template at their discretion; however, the parts of the template were designed to present the suggested and optional information in a logical manner. For a detailed description of each element and examples of statements, see the appropriate section below in this chapter.
The origin and the identity of the excipient are typically established in a Header section. The manufacturer and manufacturing site should be identified if different from the supplier and supplier location, enabling the user to make certain that the excipient comes from a qualified source. Although the manufacturer should be made known to the user, the use of codes for manufacturers and manufacturing sites on the COA to protect confidentiality is acceptable. The identity of the excipient must be definitively established by stating the compendial and trade name, the grade of the material, and applicable compendial designations.
A lot/batch number or other means of uniquely identifying the quantity of material covered by the COA and information relating specifically to it are typically included in a Body section. The lot number or other unique identification of the material, its date of manufacture, and product code or number should be stated and traceable to a specified lot. If applicable, the expiration date, recommended re-evaluation date, or other relevant statement regarding the stability of the excipient is typically included in this section. Any information required by the customer would also be included here.
The actual test results applicable to the quantity of material covered by the COA are included in an Analysis section. The test name, the result, the acceptance criteria or specifications, and a reference to the test method used should be included for each characteristic listed. Reporting of actual data and observations is recommended rather than nonspecific “passes” or “conforms” statements. If the reported results are derived from a skip-lot or reduced frequency testing program, or an average or in-process test result, this should be noted on the COA.
The Certification and Compliance Statement section is used to list various types of statements that may be required depending on the excipient and specific user needs. These statements are usually negotiated between supplier and user based on specific application requirements. Any declaration of the supplier that includes compliance of additional compendial or other regulatory requirements is typically included in this section.
Many excipients have applications other than pharmaceuticals, such as food, cosmetics, or industrial products. Any product listed as being in compliance with specific regulations should meet the specifications and requirements of that regulation and must be manufactured under appropriate GMPs.
The identity of the individual approving the content of the COA should appear on the COA. The page number and total number of pages should also appear on the COA. This information is usually included in a Footer section.
CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS TEMPLATE
Listed below is a template for the content and format of a COA.
Header
- Titled “Certificate of Analysis”
- Company Name, Address, Phone Number, and Identity of Manufacturer and Manufacturing Site
- Name (compendial/trade) of Excipient
- Grade of Excipient
- Compendial Designation
Body
- Lot/Batch Number
- Date of Manufacture
- Product Code or Number
- Expiration Date (if required)
- Recommended Re-Evaluation Date (if required)
- Stability Statement (if required)
- Customer Required Information
Analysis
- Test Name
- Test Results
- Acceptance Criteria (i.e., specifications)
- Reference to the Test Method
- Reference to Skip-Lot Testing (if appropriate)
- Reference to Average or In-Process Test Results (if appropriate)
- Date Retested (if appropriate)
- Summary of Noncompendial Testing (if any)
Certification and Compliance Statements
- GMP Compliance
- Additional Regulatory References
- Potential to Meet Additional Compendial Standards
- Content Listing and Grade of Ingredients (if a mixture)
- Other Specific Compliance Statements [e.g., organic volatile impurities (OVI), residual solvents, transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE), etc.]
Footer
- Identity of Authorized Individual for Approval
- Date of Approval
- Page Number (i.e., 1 of __)
COMPENDIAL DESIGNATION
For a supplier to claim a compendial grade on the COA for an excipient, two requirements should be met. The first requirement is that the excipient be manufactured according to recognized principles of GMPs (see General Notices and Requirements). Adequate conformance to GMPs should also be demonstrated for subsequent steps in the distribution of the excipient. The second requirement is that the excipient meet all the specifications contained in the appropriate compendial monograph, unless its difference is stated on its label, as defined under General Notices and Requirements. When an excipient is listed as compendial grade, it is understood that the above requirements have been met for the material, and the user would be able to confirm this through an appropriate audit of the supplier.
Compendial standards define what is considered an acceptable article and also give test procedures that demonstrate that the article is in compliance. These standards apply at any time in the life of the article from production to consumption. The supplier's release specifications and compliance with GMPs are developed and followed to ensure that the article, when stored according to recommended conditions, will comply with compendial standards until its expiration or recommended re-evaluation date.
Every compendial article shall be so constituted that when examined in accordance with these assay and test procedures, it meets all the requirements in the monograph defining it, as well as meeting any provisions under General Notices and Requirements and in the general chapters, as applicable. However, it is not to be inferred that application of every analytical procedure in the monograph to samples from every production batch is necessarily a prerequisite for ensuring compliance with compendial standards before the batch is released for distribution.
Data derived from manufacturing process validation studies and from in-process controls may provide greater assurance that a batch meets a particular monograph requirement than analytical data derived from examination of finished units drawn from the batch. On the basis of such assurances, the analytical procedures in the monograph may be omitted by the supplier when judging compliance of the batch with the compendial standards.
DATES ON A CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS
Part of the overall goal to standardize COA for excipients includes a provision for the consistent reporting of appropriate, meaningful, and well-defined dates. The discussion below indicates specific dates that are expected on the COA, along with definitions of the dates, in order to provide suppliers and users of excipients with a mutual understanding of their meaning. Use of the recommended terminology will be helpful in reducing the number of questions on dating information reported for excipients. Use of terminology other than that discussed below is discouraged, because the terms may be ill-defined and have different meanings for the excipient supplier and user. Examples of such terms that should not be used include “shelf life”, “use-by date”, “warranty date”, and “expiration period”.
In reporting dates on COA for excipients, it is important that a clear and unambiguous format be used to prevent possible misinterpretation. To accomplish this, it is recommended that an alpha designation be used for the month (may be abbreviated), rather than a numerical representation. It is also recommended that the year include all 4 digits (e.g., Jan. 1, 2005, or 1 Jan. 2005).
Date of Manufacture—
The date of manufacture should be included on the COA for each excipient lot and should be assigned by the suppliers on the basis of their established policies and procedures. It is recognized that excipients may be manufactured using a variety of processes (e.g., continuous or batch) that may require a period of several days or more to complete. In addition, some excipients may be mixtures or blends of other excipients, and excipient production may include reprocessing steps. Because of this diversity, the date of manufacture should be clearly defined by the supplier and consistently applied for the particular excipient and process. In reporting the date of manufacture, the excipient supplier should indicate the date of completion of the final manufacturing process (as defined by the supplier).
It is important to note that repackaging alone is not considered a processing step to be used in determining the date of manufacture. To provide traceability for a specific excipient lot, other dates may be required in addition to the date of manufacture in order to reflect additional steps such as repackaging.
Expiration Date and Recommended Re-Evaluation Date—
The stability of excipients may be an important factor in the stability of the finished pharmaceutical dosage forms that contain them. Many excipients are very stable and may not require extensive testing to demonstrate continued conformance to appropriate specifications. Other excipients may undergo chemical, physical, and microbiological changes over time that cause the material to fall outside established specifications.
Appropriate expiration and/or recommended re-evaluation dates for excipients should be established from the results of a documented stability-testing program or from historical data. The testing program should include defined and controlled storage conditions (e.g., temperature and humidity), a consideration of different packaging types that may be used as market containers, and meaningful, specific test methods to adequately assess the stability characteristics of the excipient. Stability testing should determine whether possible degradation, moisture gain or loss, viscosity changes, or other possible changes occur to make the excipient unacceptable for use (e.g., unstable or hygroscopic materials). For additional information on excipient stability, see Good Manufacturing Practices for Bulk Pharmaceutical Excipients  1078
1078 .
.
The expiration date for an excipient is defined as the date after which the supplier recommends that the material should not be used. Prior to the assigned expiration date, the excipient is expected to remain within established specifications, if stored according to the supplier's recommended conditions.
The recommended re-evaluation date for an excipient is the date suggested by the supplier after which the material should be re-evaluated to ensure continued compliance with specifications. Re-evaluation of the excipient may include physical inspection and appropriate chemical, physical, and microbiological testing. Prior to the re-evaluation date, the excipient is expected to remain within established specifications, provided it has been stored according to the supplier's recommended conditions. But beyond the recommended re-evaluation date, the excipient should not be used without adequate evaluation at appropriate intervals, to determine whether the material continues to be acceptable for use. The recommended re-evaluation date differs from the expiration date in that the excipient may be re-evaluated to extend the length of time the material may be used, if supported by the results of the evaluation and appropriate stability data.
In reporting the expiration and recommended re-evaluation dates, the excipient supplier is providing important information to the user about the stability of the material. As discussed previously, the assignment of an expiration date and a recommended re-evaluation date should be based on appropriate evaluation of potential changes that may occur in the material's properties. It is acceptable to report both an expiration date and a recommended re-evaluation date on the COA for excipients, if applicable, but both dates may not always be required. Expiration and recommended re-evaluation dates should not be reported by a supplier without sufficient stability data or product history to support the assigned dates.
For excipients determined to be very stable (greater than 2 years), either the specific expiration date and/or the recommended re-evaluation date should be reported on the COA for the material, or a general stability statement may be included (e.g., stability greater than 2 years). If available data indicate that an excipient has limited stability (2 years or less) under anticipated storage conditions, a specific expiration date and/or recommended re-evaluation date should be reported on the COA for the material.
If data from formalized stability studies are not available for an excipient, an appropriate statement should be included on the COA to indicate what is known about the stability of the material and whether stability studies are in progress.
Date Retested—
If retesting is performed by an excipient supplier and the results are used to extend the length of time that the material may be used, the date retested should also be reported on the COA. The specific tests that were subject to retesting should be clearly identified, and the results obtained upon retesting should be reported. After retesting, a new recommended re-evaluation date should be reported on the COA.
Additional Dates—
Other dates may appear on a COA, if desired by the excipient supplier or requested by the user. Examples include the release date, shipping date, date of testing, and date the COA was printed or approved. Any additional dates that appear on a COA for excipients should include a clear indication of what the date represents or means.
TESTING FREQUENCY
For the excipients listed in the USP–NF, the product specifications are set by the supplier to include all parameters listed in the monograph. It is not required that analysis of all specification parameters be made on each lot (see General Notices and Requirements). However, sufficient analysis and process validation data should exist to ensure that the lot meets all specifications before it is released. This is an established practice that has been successfully used in industry for many years. Periodic testing of all parameters should be performed to revalidate the control system. The frequency of these periodic tests should be determined by the suppliers on the basis of their understanding of the manufacturing control system. At a minimum, the parameters should be checked once a year.
For excipients that are not included in USP–NF, specifications should be set by the supplier to ensure that the quality of the material is maintained on a continuing basis and reflects both the excipient manufacturing process and inherent properties. The analytical methods used to evaluate the characteristics of noncompendial excipients may be the same as those contained in the compendia, or may be unique to the supplier or the material. The methods should be demonstrated to provide accurate, reproducible, and consistent results for the characteristic being tested. It may be appropriate for noncompendial excipients to have some tests performed at reduced frequency.
The excipient user should evaluate the supplier's specifications and methods to ensure that they are appropriate and acceptable for the quality control needed for the manufacturing process of their drug product. The user should determine which of the supplier's specifications and methods are required for release of the excipient for use in their process. If additional tests or alternative methods are required by the user, appropriate specifications and methods, along with responsibility for performing the testing, must be agreed upon by the excipient supplier and user.
Reduced Frequency Testing
When analysis of some parameters is carried out at a reduced frequency (for example, every 10th lot), this should be clearly stated on the COA. Each specific test subject to reduced frequency testing should be indicated. Reduced frequency testing should be used only for excipients manufactured using a stable process. There should be a sound technical basis and sufficient documentation to support testing any parameter at a reduced frequency. This would normally include the following points:
- Appropriate validation of the manufacturing process
- Process control—attribute charting (when appropriate)
- GMP controls
As part of the justification for reduced testing, it is important that there be assurances in place showing that the manufacturer's process complies with appropriate excipient GMP requirements.
Some tests, because of their significance, should always be performed on each lot, whereas others may be candidates for reduced frequency testing. Attribute testing results in qualitative data that provide pass/fail results or results expressed as less than or greater than a specified value. The result merely establishes compliance with a specification parameter. There are no data to indicate how well the material complies, as would be obtained from variable or quantitative test results.
Reduced frequency testing of an attribute requires that the manufacturer show that the qualitative parameter is in a state of statistical control. This necessitates tabulating the test results for consecutive lots produced.
Skip-Lot Testing—
Skip-lot testing may be applied to an excipient that is made by either a batch or a continuous process. Various commonly accepted statistical sampling plans may be used to demonstrate appropriate process control. Examples of each are listed below.
example 1: For an average outgoing quality level (AOQL) of 1% and a test frequency of 1 in 10, the supplier should find 100 consecutive lots in conformance. At a 2% AOQL and a test frequency of 1 in 10, the supplier would test 50 consecutive lots. For a 1% AOQL and a 1 in 5 test frequency, the supplier would test 70 consecutive lots. Nomographs are available to determine the test requirements.
example 2: When the excipient is manufactured by a continuous process, no discrete lot is produced. The sampling plan again is based upon the risk of approving a lot that was nonconforming. By testing 140 consecutive lots before going to a test frequency of 1 in 10, the plan establishes a low risk of approving a lot that is noncompliant.
Once the requirement is met, the supplier can monitor conformance to the specification parameter by testing 1 in 10 lots. Should any lot fail the analysis, the supplier should return to 100% testing until the results once again meet the specification above.
Because excipients vary greatly in chemical and physical properties, the supplier of the excipient should determine which tests should be routinely performed and which tests may be appropriate for reduced frequency testing. This determination must be justified and documented on the basis of the adequacy of the supplier's control system. Documentation should be kept detailing the assumptions and the data supporting the skip-lot testing plan.
Type A and Type B Tests—
Only certain types of tests are appropriate for reduced frequency testing. Type A is defined as tests that may not be easily controlled through standard process control techniques or that may change with time. These tests should normally be performed on each lot. Type B is defined as tests that normally can be controlled using standard process control techniques and that are not expected to change with time. These tests are candidates for reduced frequency testing. Examples of both types of tests are listed below.
type a: examples of tests that typically need to be performed on every lot
- Identification—Required by GMPs for users (candidate for reduced frequency testing by suppliers)
- Assay—Critical quality parameter (if specified)
- Viscosity—Usually indicates grade
- Loss on drying (or moisture determination)—Indication of stability and appropriate process controls
- Color—Indication of stability and appropriate process controls
- pH—Indication of stability and appropriate process controls
type b: examples of tests that may be candidates for reduced frequency testing
- Manufacturing impurities—Based on starting materials and processes (e.g., Chloride, Sulfate, Nitrate, Glyoxal)
- Heavy metals
- Lead
- Arsenic
- Residue on ignition
- Residual solvents
This is not meant to be an exhaustive list of tests. It simply provides some direction on how a supplier can assess the importance of each test to the overall control of the process. Tests listed as possible candidates for reduced frequency testing (Type B) may need to be routinely tested (Type A), depending on the raw materials and process. Determinations can also be made for some Type A tests to become Type B tests. In a dedicated facility, identification testing by the supplier may not be necessary.
Documentation—
The supplier of an excipient should develop and maintain documentation that outlines the process control systems and validation data to justify the use of reduced frequency testing. This documentation should also include procedures for handling the impact of significant changes on the reduced frequency testing program.
The minimum number of lots to be fully tested for all specification parameters after a change has been made depends on the process and the significance of the change and should be based on sound statistical considerations.
Additionally, the documentation should contain procedures for re-evaluating the reduced frequency testing program when a testing failure occurs. Decisions regarding the continuance of reduced frequency testing should be justified on the basis of the reasons for the failure and the supplier's ability to provide assurances that the reduced frequency testing program or other in-process parameters would identify these types of failures in the future.
Justifications for Reduced Frequency Testing—
The following are examples of situations where a sound technical basis can be demonstrated and where reduced frequency testing might therefore be justified. [note—There may be other such examples.]
- An impurity, by-product, or unreacted raw material could not be present in the product because the raw materials and chemical reactions used could not contain or generate such substances above the specified limits.
- The process capability index (Cp) on the relevant parameter is high and based on a stable process. Statistical analysis of the reduced frequency data should show that the property remains stable and within specifications. A process is considered stable when the output of the process, regardless of the nature of the processing (batch or continuous), can be demonstrated by appropriate means to show a level of variability that consistently meets all aspects of the stated specification (both Pharmacopeia-specific and customer-specific) and is thus acceptable for its intended use. For continuous processing, it is also important to demonstrate that the material has been produced under conditions in which the process has achieved a form of “steady state”, i.e., in which there is minimal operator intervention and in which the in-process parameters have been stabilized (see Appendix 2 for further definition of this concept and for determining levels of control).
- For a continuous process, the in-process analyses show that the property that is determined at reduced frequency is stable and within specification. Repeating the test on each lot would be redundant.
- An analysis that is determined on every lot has been shown to strongly correlate with an analysis that is run at a reduced frequency. The correlation shows that if a lot is within specification on the first analysis, it will be within specification on the second analysis.
USE OF ELECTRONIC SIGNATURES
Because of the growing dependence on computers and the need to accommodate paperless record systems, an electronic alternative to handwritten records and signatures is suggested. Excipient suppliers have added computer information systems to enhance productivity.
The primary issue with transfer of a COA without a handwritten signature is the validation of data. There are several considerations that should be met before an electronic signature or name attachment to a COA is considered acceptable.
- Computer systems access must be limited to authorized individuals: access is gained only after inputting a user name and a password. The system should require frequent changes of each individual password.
- A confirmation of the integrity and accuracy of the information stored in the system should be completed.
- The operation of the system must be checked routinely to ensure that the correct information is transferred from the database to the printed record.
- Data entered into a database from which information is extracted for a COA should be accompanied by time- and date-stamped audit trails.
When these criteria are met, the issuance of COAs with electronic signatures or the responsible person's name attached to the document, in lieu of a handwritten signature, is acceptable. [note—Computer systems are currently regulated by 21 CFR 11 of the FDA. Users should monitor the FDA's approach to compliance in this area.]
DISTRIBUTOR INFORMATION
The presentation of a COA issued by a distributor presents some challenges. Because COAs are important documents characterizing the excipients and the state of their quality, the source of that information becomes very important to the end user(s). Because distributors take on different roles in fulfilling the services for which they are contracted, it is necessary to ensure that procedures and methods are appropriate for the functions performed.
Distributors may function in a number of different capacities relating to the movement of excipients and to services associated with their production. Some are simply pass-through locations in which nothing is done to the excipient with the exception of storage and handling. Others serve as extensions of the manufacturer's process by taking bulk quantities and repackaging them for the manufacturer. Still others purchase excipients and repackage them under a different label for sale and distribution. These scenarios should be understood and properly documented with programs that will protect the integrity and safety of the excipients as they move through the distribution process.
Original Manufacturer and Manufacturing Site—
The identity of the original manufacturer and the manufacturing site should be included on the COA for excipients. This information is important because it provides traceability for specific excipient lots and assures the excipient users that they are consistently obtaining material from the same manufacturer and site.
Reporting the identity and location of the manufacturer does not represent an issue when the original manufacturer is also the direct supplier of the excipient to the pharmaceutical customers. However, it is recognized that this information may be considered proprietary by an excipient distributor. To adequately address this issue, excipient distributors should either list the specific information identifying the original manufacturer and location or provide the information by reporting an appropriate code, which is assigned in order to unambiguously identify the original manufacturer and manufacturing site. To protect the secrecy of this information, the meaning of the code does not have to be revealed to intermediary distributors.
Certificate of Analysis Data—
When a distributor is primarily used as a pass-through of the excipient without any changes to the excipient and packaging, the COA that accompanies the excipient from the manufacturer can be passed on in the original form. If the data are extracted, translated, or rewritten on other letterhead, a system should be in place to check the rewritten information, and justification should be demonstrated upon request. Alternatively, the source of the data should be indicated on the document.
For a distributor that takes bulk quantities of an excipient from a manufacturer and introduces the bulk quantities into a process (e.g., conveyance and storage system), analysis of the packaged excipient should be performed to demonstrate the same quality as the lot (batch) introduced. Appropriate analytical data should be included on the COA to verify the quality. The distributor should use equivalent methodology and equipment for the analytical evaluation. Some data may be used from the original manufacturer's COA with appropriate justification.
In all scenarios, it is expected that the distributor will have the appropriate level of GMP in place.
APPENDIX 1
DEFINITIONS
Acceptance Criteria—
The specifications and acceptance or rejection limits—such as acceptable quality level or unacceptable quality level with an associated sampling plan—that are necessary for making a decision to accept or reject a lot or batch of raw material, intermediate, packaging material, or excipient.
Batch (or Lot)—
A defined quantity of excipient processed so that it could be expected to be homogeneous. In a continuous process, a batch corresponds to a defined portion of the production, based on time or quantity (e.g., vessel's volume, 1 day's production, etc.).
Batch Number (or Lot Number)—
A unique and distinctive combination of numbers and/or letters from which the complete history of the manufacture, processing, packaging, coding, and distribution of a batch can be determined.
Batch Process—
A manufacturing process that produces the excipient from a discrete supply of raw materials that is present before the completion of the reaction.
Certificate of Analysis (COA)—
A document relating specifically to the results of testing a representative sample drawn from the batch of material to be delivered.
Chemical Property—
A quality parameter that is measured by chemical or physicochemical test methods.
Continuous Process—
A manufacturing process that continually produces the excipient from a continuous supply of raw material.
Contract Facility—
An internal or external facility that provides services to the manufacturer or distributor of an excipient. These can include, but are not limited to, the following: manufacturing facilities, laboratories, repackaging facilities (including labeling), and warehouses.
Date of Manufacture—
A date indicating the completion of the final manufacturing process (as defined by the supplier for the particular excipient and process).
Date Retested—
The date when retesting is performed by an excipient supplier to extend the length of time that the material may be used.
Distributor—
A party other than the manufacturer who sells the excipient.
Excipient—
Any substance, other than the active pharmaceutical ingredient or drug product, that has been appropriately evaluated for safety and is included in a drug delivery system to aid the processing of the drug delivery system during manufacture; to protect, support, or enhance stability, bioavailability, or patient acceptability; to assist in product identification; or to enhance any other attribute of the overall safety and effectiveness of the drug delivery system during storage or use.
Expiration Date—
The date after which the supplier recommends that the material should not be used.
Impurity—
Any component of an excipient that is not the intended chemical entity but is present as a consequence of either the raw materials used or the manufacturing process.
Lot—
See Batch.
Lot Number—
See Batch Number.
Manufacturer—
A party who performs the final processing step.
Packaging—
The container and its components that hold the excipient for storage and transport to the customer.
Periodic Testing Program—
See Skip-Lot Testing Program.
Physical Property—
A quality parameter that can be measured solely with mechanical equipment.
Process—
The set of operating instructions describing how the excipient is to be synthesized, isolated, purified, etc.
Process Capability Index (Cp)—
A statistical measurement that can be used to assess whether the process is adequate to meet specifications. A state of statistical control can be said to exist if the random variation in test results for a process parameter is such that the calculated process capability is greater than 1.33 (see Appendix 2 for further definition).
Process Step—
An instruction to the excipient manufacturing personnel directing that an operation be performed.
Recommended Re-Evaluation Date—
The date suggested by the supplier when the material should be re-evaluated to ensure continued compliance with specifications. Differs from the Expiration Date in that the excipient may be re-evaluated to extend the length of time the material may be used, if supported by the results of the evaluation and appropriate stability data.
Reduced Frequency Testing Program—
See Skip-Lot Testing.
Repackaging—
Transfer of an excipient from one container to another.
Reprocessing—
Introducing previously processed material that did not conform to standards or specifications back into the process and repeating steps that are already part of the normal manufacturing process.
Significant Change—
Any change that alters an excipient's physical or chemical property from the norm or that is likely to alter the excipient's performance in the dosage form.
Site—
A location where the excipient is manufactured. This may be within the facility but in a different operational area, or at a remote facility, including a contract manufacturer.
Skip-Lot Testing Program—
Periodic or intermittent testing performed for a particular test parameter that is justified by historical data demonstrating a state of statistical process control.
Specification—
The quality parameters to which the excipient, component, or intermediate must conform and that serve as a basis for quality evaluation.
Stable Process—
A process whose output, regardless of the nature of the processing (batch or continuous), can be demonstrated by appropriate means to show a level of variability that consistently meets all aspects of the stated specification (both USP-specific and customer-specific) and is thus acceptable for its intended use.
Supplier—
A manufacturer or distributor who directly provides the excipient to the user.
User—
A party who uses an excipient in the manufacture of a drug product or another excipient.
APPENDIX 2
STATE OF STATISTICAL CONTROL: PROCESS CAPABILITY PARAMETERS FOR DETERMINING LEVELS OF CONTROL
A process is considered to be in a state of statistical control if variations among the observed sampling results from the process can be attributed to a constant system of chance causes. Process capability index (Cp) or capability index adjusted for the process average (Cpk) or performance index (Pp) or performance index adjusted for the process average (Ppk) can be used to assess whether the process is adequate to meet specifications. Values of these parameters exceeding 1.33 show that the process is adequate to meet specifications. Values between 1.00 and 1.33 indicate that the process, although adequate to meet specifications, will require close control. Values below 1.00 indicate that the process is not adequate to meet specifications and that the process and/or specifications should be changed. Pp/Ppk will always be less than or equal to Cp/Cpk, respectively. The essential difference between the capability and the performance indices is the data used. Capability indices require the calculation of 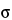 , the population standard deviation, whereas the performance indices require the calculation of s, the sample standard deviation. Thus for pharmaceutical excipients a state of statistical control can be said to exist if the random variation in test results for a process parameter is such that the calculated process capability index or performance index is greater than 1.33.
, the population standard deviation, whereas the performance indices require the calculation of s, the sample standard deviation. Thus for pharmaceutical excipients a state of statistical control can be said to exist if the random variation in test results for a process parameter is such that the calculated process capability index or performance index is greater than 1.33.
Auxiliary Information— Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| General Chapter | Robert H. Lafaver, B.A.
Scientist 1-301-816-8335 |
(EGC05) Excipient General Chapters |
USP32–NF27 Page 541
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(4) Page 1167