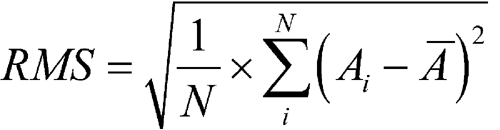INTRODUCTION
Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy is a branch of vibrational spectroscopy that shares many of the principles that apply to other spectroscopic measurements. The NIR spectral region comprises two subranges associated with detectors used in the initial development of NIR instrumentation. The short-wavelength (Herschel or silicon region) extends from approximately 780 to 1100 nm (12,821–9000 cm–1); and longer wavelengths, between 1100 and 2500 nm, compose the traditional (lead sulfide) NIR region. Applications of NIR spectroscopy use spectra displayed in either wavelength or wavenumber units. As is the case with other spectroscopy measurements, interactions between NIR radiation and matter provide information that can be for both qualitative and quantitative assessment of the chemical composition of samples. In addition, qualitative and quantitative characterization of a sample's physical properties can be made because of the sample's influence on NIR spectra. Measurements can be made directly on samples in situ in addition to applications during standard sampling and testing procedures.
Applications of qualitative analysis include identification of raw material, in-process sample, or finished product. These applications often involve comparing an NIR spectrum from a sample to reference spectra and assessing similarities against acceptance criteria developed and validated for a specific application. In contrast, applications of quantitative analysis involve the development of a predictive relationship between NIR spectral attributes and sample properties. These applications typically use numerical models to quantitatively predict chemical and/or physical properties of the sample on the basis of NIR spectral attributes.
Vibrational spectroscopy in the NIR region is dominated by overtones and combinations that are much weaker than the fundamental mid-IR vibrations from which they originate. Because molar absorptivities in the NIR range are low, radiation can penetrate several millimeters into materials, including solids. Many materials, such as glass, are relatively transparent in this region. Fiber-optic technology is readily implemented in the NIR range, which allows monitoring of processes in environments that might otherwise be inaccessible.
The instrument qualification tests and acceptance criteria provided in this chapter may not be appropriate for all instrument configurations. In such cases, alternative instrument qualification and performance checks should be scientifically justified and documented. In addition, validation parameters discussed in this chapter may not be applicable for all applications of NIR spectroscopy. Validation parameters characterized for a specific NIR application should demonstrate suitability of the NIR application for its intended use.
Transmission and Reflection
The most common measurements performed in the NIR spectral range are transmission and reflection spectroscopy. Incident NIR radiation is absorbed or scattered by the sample and is measured as transmittance or reflectance, respectively. Transflection spectrometry is a hybrid of transmission and reflection wherein a reflector is placed behind the sample so that the optical path through the sample and back to the detector is doubled compared to a transmission measurement of a sample of the same thickness. Transflection is used to describe any double-pass transmission technique. The light may be reflected from a diffuse or specular (mirror) reflector placed behind the sample. This configuration can be adapted to share instrument geometry with certain reflection or fiber-optic probe systems in which the source and the detector are on the same side of the sample.
transmittance, T, is a measure of the decrease in radiation intensity as a function of wavelength when radiation is passed through a sample. The sample is placed in the optical beam between the source and the detector. The results of both transmission and transflection measurements are usually presented directly in terms of absorbance, i.e., log10(1/T).
reflectance, R, is a measure of the ratio of the intensity of light reflected from the sample, I, to that reflected from a background or reference reflective surface, IR. Most reflection measurements in the NIR are made of scattering samples such as powders and slurries. For such materials NIR radiation can penetrate a substantial distance into the sample, where it can be absorbed when the wavelength of the radiation corresponds to a transition between the ground vibrational state of the analyte and either a harmonic of a given vibrational mode (an overtone) or the sum of two or more different modes (a combination band). Nonabsorbed radiation is scattered back from the sample to the detector. NIR reflection spectra are accessed by calculating and plotting log(1/R) versus wavelength. This logarithmic form is the pseudo-absorbance of the material and is commonly called absorbance.
Factors That Affect NIR Spectra
The following list is not exhaustive, but it includes many of the major factors that affect NIR spectra.
Sample Temperature—
Sample temperature influences spectra obtained from aqueous solutions and other hydrogen-bonded liquids, and a difference of a few degrees may result in significant spectral changes. Temperature may also affect spectra obtained from less polar liquids, as well as solids that contain solvents and/or water.
Moisture and Solvent—
Moisture and solvent present in the sample material and analytical system may change the spectrum of the sample. Both absorption by moisture and solvent and their influence on hydrogen bonding of the APIs and excipients can change the NIR spectrum.
Sample Thickness—
Sample thickness is a known source of spectral variability and must be understood and/or controlled. The sample thickness in transmission mode is typically controlled by using a fixed optical path length for the sample. In diffuse reflection mode, the sample thickness is typically controlled by using samples that are “infinitely thick” relative to the detectable penetration depth of NIR light into a solid material. Here “infinite thickness” implies that the reflection spectrum does not change if the thickness of the sample is increased.
Sample Optical Properties—
In solids, both surface and bulk scattering properties of calibration standards and analytical samples must be taken into account. Surface morphology and refractive index properties affect the scattering properties of solid materials. For powder materials, particle size and bulk density influence scattering properties and the NIR spectrum.
Polymorphism—
Variation in crystalline structure (polymorphism) from materials with the same chemical composition can influence NIR spectral response. Different polymorphs and amorphous forms of solid material may be distinguished from one another on the basis of their NIR spectral properties. Similarly, different crystalline hydration or solvation states of the same material can display different NIR spectral properties.
Age of Samples—
Samples may exhibit changes in their chemical, physical, or optical properties over time. Care must be taken to ensure that both samples and standards used for NIR analysis are suitable for the intended application.
INSTRUMENTATION
Apparatus
All NIR measurements are based on exposing material to incident NIR light radiation and measuring the attenuation of the emerging (transmitted, scattered, or reflected) light. Several spectrophotometers are available; they are based on different operating principles—for example: filters, grating-based dispersive, acousto-optical tunable filter (AOTF), Fourier–transform NIR (FT–NIR), and liquid crystal tunable filter (LCTF). Silicon, lead sulfide, indium gallium arsenide, and deuterated triglycine sulphate are common detector materials. Conventional cuvette sample holders, fiber-optic probes, transmission dip cells, and spinning or traversing sample holders are common examples of sample interfaces for introducing the sample to the optical train of a spectrometer.
The selection of specific NIR instrumentation and sampling accessories should be based on the intended application, and particular attention should be paid to the suitability of the sampling interface for the type of sample that will be analyzed.
Near-Infrared Reference Spectra
NIR references, by providing known stable measurements to which other measurements can be compared, are used to minimize instrumental variations that would affect the measurement.
Transmittance—
The measurement of transmittance requires a background reference spectrum for determining the absorption by the sample relative to the background. Suitable transmittance reference materials depend on the specific NIR application and include air, an empty cell, a solvent blank, or a reference sample.
Reflectance—
The measurement of reflectance requires the measurement of a reference reflection spectrum to determine the attenuation of reflected light relative to the unattenuated incident beam. The reflectance spectrum is calculated as the ratio of the single-beam spectrum of the sample to that of the reference material. Suitable reflectance reference materials depend on the specific NIR application and include ceramic, perfluorinated polymers, gold, and other suitable materials.
Qualification of NIR Instruments
Qualification—
Qualification of an NIR instrument can be divided into three elements: Installation Qualification (IQ); Operational Qualification (OQ); and Performance Qualification (PQ). For further discussion, see the proposed general information chapter Analytical Instrument Qualification  1058
1058 .
.
Installation Qualification—
The IQ requirements help ensure that the hardware and software are installed to accommodate safe and effective use of the instrument at the desired location.
Operational Qualification—
In operational qualification, an instrument's performance is characterized using standards to verify that the system operates within target specifications. The purpose of operational qualification is to demonstrate that instrument performance is suitable. Because there are so many different approaches for measuring NIR spectra, operational qualification using standards with known spectral properties is recommended. Using external traceable reference standard materials does not justify omitting the instrument's internal quality control procedures. As is the case with any spectroscopic device, wavelength uncertainty, photometric linearity, and noise characteristics of NIR instruments should be qualified against target specifications for the intended application.
Performance Qualification—
Performance qualification demonstrates that the NIR measurement consistently operates within target specifications defined by the user for a specific application; it is often referred to as system suitability. Performance qualification for NIR measurements can include comparing a sample or standard spectrum to previously recorded spectra. Comparisons of spectra taken over time from identical and stable samples or reference standard materials can form the basis for evaluating the long-term stability of an NIR measurement system. The objective is to demonstrate that no abnormal wavelength shift or change in detector sensitivity has occurred during ongoing analysis.
Characterizing Instrument Performance—
Specific procedures, acceptance criteria, and time intervals for characterizing NIR instrument performance depend on the instrument and intended application. Many NIR applications use previously validated models that relate NIR spectral response to a physical or chemical property of interest. Demonstrating stable instrument performance over extended periods of time provides some assurance that reliable measurements can be taken from sample spectra using previously validated NIR models.
Wavelength Uncertainty—
NIR spectra from sample and/or reference standard materials can be used to demonstrate an instrument's suitable wavelength dispersion performance against target specifications. The USP Near IR System Suitability Reference Standard or the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Standard Reference Material (SRM) 2036 for reflectance measurement and NIST SRM 2035 for transmittance measurement can be used for wavelength verification. Suitable materials for demonstrating wavelength dispersion performance include polystyrene, mixtures of rare earth oxides, and absorption by water vapor for instruments that use an interferometer for wavelength dispersion. With appropriate justification, alternative standards may be used. Wavelength uncertainty typically is characterized from a single spectrum (collected with the same spectral resolution to obtain the standard value) using a minimum of three peaks that cover a suitable spectral range of the instrument. Typical tolerances for agreement with standard values are ±1.0 nm from approximately 700 to 2000 nm and ±1.5 nm above 2000 nm to approximately 2500 nm (±8 cm–1 below 5000 cm–1 and ±4 cm–1 from 5000 cm–1 to approximately 14,000 cm–1). Alternative tolerances may be used when justified for specific applications.
Photometric Linearity and Response Stability—
NIR spectra from samples and/or reference standard materials with known relative transmittance or reflectance can be used to demonstrate a suitable relationship between NIR light attenuation (due to absorption) and instrument response. For reflectance measurements, commercially-available reflectance standards with known reflectance properties are often used. Spectra obtained from reflection standards are subject to variability as a result of the difference between the experimental conditions under which they were factory calibrated and those under which they are subsequently put to use. Hence, the reflectance values supplied with a set of calibration standards may not be useful in the attempt to establish an “absolute” calibration for a given instrument. Provided that (1) the standards do not change chemically or physically, (2) the same reference background is also used to obtain the standard values, and (3) the instrument measures each standard under identical conditions (including precise sample positioning), the reproducibility of the photometric scale will be established over the range of standards. Subsequent measurements on the identical set of standards give information on long-term stability. Photometric linearity is typically characterized using a minimum of four reference standards in the range from 10% to 90% reflection (or transmission). NIR applications based on measuring an absorbance larger than 1.0 may require standards with reflectivity properties between 2% and 5% reflection (or transmission) for characterizing instrument performance at low reflectance. The purpose is to demonstrate a linear relationship between NIR reflectance and/or transmittance and instrument response over the scanning range of the instrument. Typical tolerances for a linear relationship are 1.00 ± 0.05 for the slope and 0.00 ± 0.05 for the intercept of a plot of the measured photometric response versus standard photometric response. Alternative tolerances may occur when justified for specific applications.
Spectroscopic Noise—
NIR instrument software may include built-in procedures to automatically determine system noise and to provide a statistical report of noise or S/N over the instrument's operating range. In addition, it may be desirable to supplement such checks with measurements that do not rely directly on manufacturer-supplied procedures. Typical procedures involve measuring spectra of traceable reference materials with high and low reflectance. Tolerances for these procedures should demonstrate suitable S/N for the intended application.
high-flux noise—Instrument noise is evaluated at high-light flux by measuring reflectance or transmittance of the reference standard, with the reference material (e.g., 99% reflection standard) acting as both the sample and the background reference.
low-flux noise—The same procedure may be used with a lower-reflectivity reference material (e.g., 10% reflectance standard) to determine system noise at reduced light flux. The source, optics, detector, and electronics make significant contributions to the noise under these conditions.
METHOD VALIDATION
Introduction
The objective of NIR method validation, as is the case with the validation of any analytical procedure, is to demonstrate that the measurement is suitable for its intended purpose. NIR spectroscopy is somewhat different from conventional analytical techniques because validation of the former generally is achieved by the assessment of chemometric parameters, but these parameters can still be related to the fundamental validation characteristics required for any analytical method.
Data pretreatment is often a vital step in the chemometric analysis of NIR spectral data. Data pretreatment can be defined as the mathematical transformation of NIR spectral data to enhance spectral features and/or remove or reduce unwanted sources of variation prior to using the spectrum. Calibration is the process of developing a mathematical relationship between NIR spectral response and properties of samples. Many suitable chemometric algorithms for data pretreatment and calibration exist; the selection should be based on sound scientific judgment and suitability for the intended application.
Validation Parameters
Performance characteristics that demonstrate the suitability of NIR methods are similar to those required for any analytical procedure. A discussion of the applicable general principles is found in Validation of Compendial Procedures  1225
1225 . These principles should be considered typical for NIR procedures, but exceptions should be dealt with on a case-by-case basis. For qualitative NIR methods, see chapter
. These principles should be considered typical for NIR procedures, but exceptions should be dealt with on a case-by-case basis. For qualitative NIR methods, see chapter  1225
1225 , Data Elements Required for Validation, Category IV assays. For quantitative NIR methods, see chapter
, Data Elements Required for Validation, Category IV assays. For quantitative NIR methods, see chapter  1225
1225 , Data Elements Required for Validation, Category I and Category II assays. Specific acceptance criteria for each validation parameter must be consistent with the intended use of the method. The samples for validation should be independent of the calibration set.
, Data Elements Required for Validation, Category I and Category II assays. Specific acceptance criteria for each validation parameter must be consistent with the intended use of the method. The samples for validation should be independent of the calibration set.
Specificity—
The extent of specificity testing depends on the intended application. Demonstration of specificity in NIR methods is typically accomplished by using the following approaches:
Qualitative—
Identification testing is a common application of qualitative NIR spectroscopy. Identification is achieved by comparing a sample spectrum to a reference spectrum or a library of reference spectra. The specificity of the NIR identification method is demonstrated by obtaining positive identification from samples coupled with negative results from materials that should not meet criteria for positive identification. Materials to demonstrate specificity should be based on sound scientific judgment and can include materials similar in visual appearance, chemical structure, or name.
Quantitative—
Quantitative applications of NIR spectroscopy typically involve establishing a mathematical relationship between NIR spectral response and a physical or chemical property of interest. Demonstrating specificity against a physical or chemical property of interest is based on interpreting both NIR spectral attributes and chemometric parameters in terms of the intended application and may include the following:
- Spectral regions in the calibration model can be correlated to a known NIR spectral response associated with the property of interest.
- Wavelengths used by regression analysis for the calibration (e.g., for multiple linear regression [MLR] models) or the loading vector for each factor (e.g., for partial least squares [PLS] or principal component regression [PCR] models) can be examined to verify relevant spectroscopic information that is used for the mathematical model.
- Variation in spectra from samples for calibration can be examined and interpreted as expected spectral observations.
- Variation in material composition and sample matrix may be shown to have no significant effect on quantification of the property of interest within the specified method range.
Linearity—
Quantitative NIR methods generally attempt to demonstrate a linear relationship between NIR spectral response and the property of interest. Although demonstrating a linear response is not required for all NIR applications, the model chosen, whether linear or not, should properly represent the relationship.
Validation of linearity in NIR methods may be accomplished by examining a plot of NIR spectral response versus actual or accepted values for the property of interest. Many statistical methods are available for evaluation of the goodness of fit of the linear relationship. Other applicable statistics and graphical methods may be as appropriate.
The correlation coefficient, r, may not be an informative measure of linearity. The square of the (Pearson) correlation coefficient is a measure of the fraction of the data's variation that is adequately modeled by the equation. Linearity depends on the standard error of the calibration equation (and hence the reference method) and on the range of the calibration data. Thus, although values very near 1.00, such as 0.99 or greater, typically indicate a linear relationship, lower values do not distinguish between nonlinearity and variability around the line.
Range—
The specified range of an NIR method depends on the specific application. The range typically is established by confirming that the NIR method provides suitable measurement capability (accuracy and precision) when applied to samples within extreme limits of the NIR measurement. Controls must be used to ensure that results outside the validated range are not accepted. In certain circumstances, it may not be possible or desirable to extend the validated range to include sample variability outside the validated range. Extending the range of an NIR method requires demonstration of suitable measurement capability within the limits of the expanded range. Examples of situations in which only a limited sample range may be available are samples from a controlled manufacturing process and in-process samples. A limited method range does not preclude the use of an NIR method.
Accuracy—
Accuracy in NIR methods is demonstrated by showing the closeness of agreement between the value that is accepted as either a conventional true value or an accepted reference value. Accuracy can be determined by direct comparison between NIR validation results and actual or accepted reference values. Suitable agreement between NIR and reference values is based on required measurement capability for a specific application. The purpose is to demonstrate a linear relationship between NIR results and actual values. Accuracy can be determined by agreement between the standard error of prediction (SEP) and the standard error of the reference method for validation. The error of the reference method may be known on the basis of historical data, through validation results specific to the reference method, or by calculating the standard error of the laboratory (SEL). Suitable agreement between SEP and SEL is based on required measurement capability for a specific application.
Precision—
The precision of an NIR method expresses the closeness of agreement between a series of measurements under prescribed conditions. Two levels of precision should be considered: repeatability and intermediate precision. The precision of an NIR method typically is expressed as the relative standard deviation of a series of NIR method results and should be suitable for the intended application. Demonstration of precision in NIR methods may be accomplished using the following approaches:
Repeatability—
Repeatability can be demonstrated by the following:
- Statistical evaluation of a number of replicate measurements of the sample without repositioning the sample between each individual spectral acquisition, or
- Statistical evaluation of multiple NIR method results, each result from a replicate analysis of a sample subsequent to re-positioning between spectral acquisitions
Intermediate Precision—
Intermediate precision can be shown by the following:
- Statistical evaluation of a number of replicate NIR measurements of the same or similar samples in the Repeatability study by different analysts on different days.
Robustness—
NIR measurement parameters selected to demonstrate robustness will vary depending on the application and the sample's interface with the NIR instrument. Critical measurement parameters associated with robustness often are identified and characterized during method development. Typical measurement parameters include the following:
- Effect of environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity, and vibration)
- Effect of sample temperature
- Sample handling (e.g., probe depth, compression of material, sample depth/thickness, sample presentation)
- Influence of instrument changes (e.g., lamp change, warm-up time)
Ongoing Method Evaluation
Validated NIR methods should be subject to ongoing performance evaluation, which may include monitoring accuracy, precision, and other suitable method parameters. If performance is unacceptable, corrective action is necessary. It involves conducting an investigation to identify the cause of change in method performance and may indicate that the NIR method is not suitable for continued use. Improving the NIR method to meet measurement suitability criteria may require additional method development and documentation of validation experiments demonstrating that the improved method is suitable for the intended application. The extent of revalidation required depends on the cause of change in method performance and the nature of corrective action required in order to establish suitable method performance. Appropriate change controls should be implemented to document ongoing method improvement activities.
Revalidation of a qualitative model may be necessary as a result of the following:
- Addition of a new material to the spectral reference library
- Changes in the physical properties of the material
- Changes in the source of material supply
- Identification of previously unknown critical attribute(s) of material(s)
Revalidation of a quantitative model may be necessary as a result of the following:
- Changes in the composition of the test sample or finished product
- Changes in the manufacturing process
- Changes in the sources or grades of raw materials
- Changes in the reference analytical method
- Major changes in instrument hardware
Outliers—
Sample spectra that produce an NIR response that differs from the qualitative or quantitative calibration model may produce an outlier. This does not necessarily indicate an out-of-specification result; but rather an outlier indicates that further testing of the sample may be required and is dependent on the particular NIR method. If subsequent testing of the sample by an appropriate method indicates that the property of interest is within specifications, then the sample meets its specifications. Outlier samples may be incorporated into an updated calibration model subsequent to execution and documentation of suitable validation studies.
Method Transfer
Controls and measures for demonstrating the suitability of NIR method performance following method transfer are similar to those required for any analytical procedure. Exceptions to general principles for conducting method transfer for NIR methods should be justified on a case-by-case basis. The transfer of an NIR method is often performed by using an NIR calibration model on a second instrument that is similar to the primary instrument used to develop and validate the method. When a calibration model is transferred to another instrument, procedures and criteria must be applied to demonstrate that the calibration model meets suitable measurement criteria on the second instrument. The selection of an appropriate calibration model transfer procedure should be based on sound scientific judgment.
GLOSSARY
absorbance, A, is represented by the equation:
A = –log T = log (1/T)
where T is the transmittance of the sample. Absorbance is also frequently given as:
A = log (1/R)
where R is the reflectance of the sample.
background spectrum is used for generating a sample spectrum with minimal contributions from instrument response. It is also referred to as a reference spectrum or background reference. The ratio of the sample spectrum to the background spectrum produces a transmittance or reflectance spectrum dominated by NIR spectral response associated with the sample. In reflection measurements, a highly reflective diffuse standard reference material is for the measurement of the background spectrum. For transmission measurement, the background spectrum may be measured with no sample present in the spectrometer or using a cell with the solvent blank or a cell filled with appropriate reference material.
calibration model is a mathematical expression to relate the response from an analytical instrument to the properties of samples.
diffuse reflectance is the ratio of the spectrum of radiated light penetrating the sample surface, interacting with the sample, passing back through the sample's surface, and reaching the detector to the background spectrum. This is the component of the overall reflectance that produces the absorption spectrum of the sample.
fiber-optic probes consist of two components: optical fibers that may vary in length and in the number of fibers and a terminus, which contains specially designed optics for examination of the sample matrix.
installation qualification is the documented collection of activities necessary to establish that an instrument is delivered as designed and specified, is properly installed in the selected environment, and that this environment is suitable for the instrument's intended purpose.
instrument bandwidth or resoluton is a measure of the ability of a spectrometer to separate radiation of similar wavelengths.
multiple linear regression is a calibration algorithm to relate the response from an analytical instrument to the properties of samples. The distinguishing feature of this algorithm is the use of a limited number of independent variables. Linear-least-squares calculations are performed to establish a relationship between these independent variables and the properties of the samples.
operational qualification is the process by which it is demonstrated and documented that an instrument performs according to specifications and that it can perform the intended task. This process is required following any significant change such as instrument installation, relocation, or major repair.
overall reflectance is the sum of diffuse and specular reflectance.
partial least squares (pls) is a calibration algorithm to relate instrument responses to the properties of samples. The distinguishing feature of this algorithm is that data concerning the properties of the samples for calibration are used in the calculation of the factors to describe instrument responses.
performance qualification is the process of using one or more well-characterized and stable reference materials to verify consistent instrument performance. Performance qualification may employ the same or different standards for different performance characteristics.
photometric linearity, also referred to as photometric verification, is the process of verifying the response of the photometric scale of an instrument.
principal component regression (pcr) is a calibration algorithm to relate the response from an analytical instrument to the properties of samples. This algorithm, which expresses a set of independent variables as a linear combination of factors, is a method of relating these factors to the properties of the samples for which the independent variables were obtained.
pseudo-absorbance, A, is represented by the equation:
A = –log R = log (1/R)
where R is the diffuse reflectance of the sample.
reference spectrum—See Background Spectrum.
reflectance is described by the equation:
R = I/IR
in which I is the intensity of radiation reflected from the surface of the sample and IR is the intensity of radiation reflected from a background reference material and its incorporated losses due to solvent absorption, refraction, and scattering.
root-mean-square (rms) noise is calculated by the equation:
in which Ai is the absorbance for each data point; A is the mean absorbance over the spectral segment; and N is the number of points per segment.
spectral reference library is a collection of spectra of known materials for comparison with unknown materials. The term is commonly used in connection with qualitative methods of spectral analysis (e.g., identification of materials).
specular (surface) reflectance is the reflectance of the front surface of the sample.
standard error of calibration (sec) is a measure of the capability of a model to fit reference data. SEC is the standard deviation of the residuals obtained from comparing the known values for each of the calibration samples to the values that are calculated from the calibration. SEC should not be used as an assessment tool for the expected method accuracy (trueness and precision of prediction) of the predicted value of future samples. The method accuracy should generally be verified by calculating the standard error of prediction (SEP), using an independent validation set of samples. An accepted method is to mark a part of the calibration set as the validation set. This set is not fully independent but can be used as an alternative for the determination of the accuracy.
standard error of cross-validation (SECV) is the standard deviation calculated using the leave-one-out method. In this method, one calibration sample is omitted from the calibration, and the difference is found between the value for this sample calculated from its reference value and the value obtained from the calibration calculated from all the other samples in the set. This process is repeated for all samples in the set, and the SECV is the standard deviation of the differences calculated for all the calibration samples. This procedure can also be performed with a group of samples. Instead of leaving the sample out, a group of samples is left out. The SECV is a measure of the model accuracy that one can expect when measuring future samples if not enough samples are available for the SEP to be calculated from a completely independent validation set.
standard error of the laboratory (sel) is a calculation based on repeated readings of one or more samples to estimate the precision and/or accuracy of the reference laboratory method, depending on how the data were collected.
standard error of prediction (sep) is a measure of model accuracy of an analytical method based on applying a given calibration model to the spectral data from a set of samples different from but similar to those used to calculate the calibration model. SEP is the standard deviation of the residuals obtained from comparing the values from the reference laboratory to those from the method under test for the specified samples. SEP provides a measure of the model accuracy expected when one measures future samples.
surface reflectance, also known as specular reflection, is that portion of the radiation not interacting with the sample but simply reflecting back from the sample surface layer (sample–air interface).
transflection is a transmittance measurement technique in which the radiation traverses the sample twice. The second time occurs after the radiation is reflected from a surface behind the sample.
transmittance is represented by the equation:
T = I/I0 or T = 10A
in which I is the intensity of the radiation transmitted through the sample; I0 is the intensity of the radiant energy incident on the sample and includes losses due to solvent absorption, refraction, and scattering; and A is the absorbance.
Auxiliary Information— Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| General Chapter | Gary E. Ritchie, M.Sc.
Scientific Fellow 1-301-816-8353 |
(GC05) General Chapters 05 |
USP32–NF27 Page 622
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 33(4) Page 737