Iopamidol
Change to read:
1,3-Benzenedicarboxamide, N,N¢-bis[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl]-5-[(2-hydroxy-1-oxopropyl)amino]-2,4,6-triiodo-, (S)-.
(S)-N,N¢-Bis[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl]-2,4,6-triiodo-5-lactamidoisophthalamide
» Iopamidol contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 101.0 percent of iopamidol, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers. Store at 25 , excursions permitted between 15
, excursions permitted between 15 and 30
and 30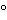 .
.
Change to read:
USP Reference standards USP Iopamidol RS.
USP Iopamidol Related Compound A RS.
USP Iopamidol Related Compound C RS.
Change to read:
Identification—
B:
Heat about 500 mg in a suitable crucible: violet vapors are evolved.
C:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the  Identification solution
Identification solution USP32 corresponds to that
USP32 corresponds to that  of the iopamidol peak
of the iopamidol peak USP32 observed in the chromatogram of the System suitability solution, as obtained in the test for Related compounds.
USP32 observed in the chromatogram of the System suitability solution, as obtained in the test for Related compounds.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
between
:
between  4.6
4.6 and
and  5.2
5.2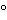 (t = 20
(t = 20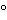 ;
; 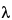 = 436 nm).
= 436 nm).
Test solution:
400 mg per mL, in water, heating on a water bath, if necessary to effect solution, and passing through a membrane filter having a 3-µm or finer porosity.
Loss on drying  731
731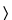 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 4 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
for 4 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Free aromatic amine—
Transfer 500 mg to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and add 20 mL of water, heating on a water bath, if necessary, to effect solution. To a second 25-mL volumetric flask transfer 18.4 mL of water and 1.6 mL of a Standard solution prepared by dissolving a suitable quantity of USP Iopamidol Related Compound A RS in water and diluting with water to obtain a solution having a concentration of 62.5 µg per mL. To a third 25-mL volumetric flask add 20 mL of water to provide a blank. Treat each flask as follows. Place the flasks in an ice bath, protected from light, for 5 minutes. [note—In conducting the following steps, keep the flasks in the ice bath and protected from light as much as possible until all of the reagents have been added.] Add slowly 1 mL of hydrochloric acid, mix, and allow to stand for 5 minutes. Add 1 mL of sodium nitrite solution (1 in 50), mix, and allow to stand for 5 minutes. Add 1 mL of ammonium sulfamate solution (3 in 25), shake, and allow to stand for 5 minutes. [Caution—Considerable pressure is produced.
] Add 1 mL of N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride solution (1 in 1000), and mix. Remove the flasks from the ice bath, and allow to stand in a water bath at about 25 for 10 minutes. Dilute with water to volume, mix, and without delay (about 5 minutes from final dilution), concomitantly determine the absorbances of the solution from the substance under test and the Standard solution in 1-cm cells at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at about 500 nm, with a suitable spectrophotometer, against the prepared blank. The absorbance of the solution from the Iopamidol is not greater than that of the Standard solution (0.02%).
for 10 minutes. Dilute with water to volume, mix, and without delay (about 5 minutes from final dilution), concomitantly determine the absorbances of the solution from the substance under test and the Standard solution in 1-cm cells at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at about 500 nm, with a suitable spectrophotometer, against the prepared blank. The absorbance of the solution from the Iopamidol is not greater than that of the Standard solution (0.02%).
Free iodine—
Transfer 2.0 g to a stoppered, 50-mL centrifuge tube, add sufficient water to dissolve, heating on a water bath, if necessary, to effect solution, and dilute with water to 25 mL. Add 5 mL of toluene and 5 mL of 2 N sulfuric acid, shake well, and centrifuge: the toluene layer shows no red color.
Limit of free iodide—
Transfer about 6.0 g, accurately weighed, to a suitable container, dissolve in 50 mL of water, and add 2.0 mL of 0.001 M potassium iodide. Titrate with 0.001 N silver nitrate VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically, using a silver indicator electrode and an appropriate reference electrode. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.001 N silver nitrate is equivalent to 126.9 µg of iodide. Not more than 0.001% is found.
Free acid or alkali—
Dissolve 10.0 g in 100 mL of freshly boiled and cooled water. Using a pH meter and a glass–calomel electrode system, determine the volume of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid VS or 0.01 N sodium hydroxide VS to bring the pH of the test solution to 7.0: not more than 1.37 mL of 0.01 N sodium hydroxide, equivalent to a free acid content of 5 mg of hydrochloric acid per 100 g, or not more than 0.75 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid, equivalent to a free alkali content of 3 mg of sodium hydroxide per 100 g, is required.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
not more than 0.001%.
:
not more than 0.001%.
Change to read:
Related compounds—
Solution B—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of water and acetonitrile (1:1).
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
System suitability solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Iopamidol RS and USP Iopamidol Related Compound C RS in water, and dilute with water to obtain a solution having concentration of about 20 µg per mL of each.
Standard solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Iopamidol RS and USP Iopamidol Related Compound C RS in water, and dilute with water to obtain a solution having concentrations of about 20 µg per mL and 50 µg per mL, respectively.
Test solution—
Transfer about 0.5 g of Iopamidol, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, add water to volume, and mix.
Identification solution—
Dilute a suitable volume of the Test solution with water to obtain a solution with a concentration of iopamidol of about 20 µg per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 240-nm detector and two 4.6-mm × 25-cm columns that contain packing L11, connected in series. The column temperature is maintained at 60
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 240-nm detector and two 4.6-mm × 25-cm columns that contain packing L11, connected in series. The column temperature is maintained at 60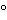 , and the flow rate is about 2.0 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
, and the flow rate is about 2.0 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between iopamidol related compound C and iopamidol is not less than 2.0. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the tailing factor for each peak is between 0.7 and 1.5, and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections for either of the two peaks is not more than 2.0%. Chromatograph the Identification solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure to obtain a chromatogram for Identification test C.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
|
| 0–18 | 100 | 0 | isocratic |
| 18–40 | 100®62 | 0®38 | linear gradient |
| 40–45 | 62®50 | 38®50 | linear gradient |
| 45–50 | 50®100 | 50®0 | linear gradient |
| 50–60 | 100 | 0 | isocratic |
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Identification solution, the System suitability solution, the Standard solution, and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak area responses.
Calculate the total percentage of iopamidol related compound C and 2-chloro derivative in the portion of Iopamidol taken by the formula:
100(C1V/W)(ri / rS)
in which C1 is the concentration, in mg per mL, of iopamidol related compound C in the Standard solution; V is the volume of the Test solution; W is the weight of Iopamidol used to prepare the Test solution; ri is the total peak response for the iopamidol related compound C and 2-chloro derivative obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the peak response for iopamidol related compound C obtained from the Standard solution.
Calculate the total percentage of any other impurity in the portion of Iopamidol taken by the formula:
100(C2V/W)(ri / rS)
in which C2 is the concentration of iopamidol, in mg per mL, in the Standard solution; V and W are as previously defined; ri is the peak response for the individual impurity obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the peak response for iopamidol obtained from the Standard solution. In addition to not exceeding the limits for each impurity shown in Table 1, not more than 0.1% of any other individual impurity is found; and not more than 0.20% of total impurities, other than iopamidol related compound C and 2-chloro derivative, is found.
Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Limit (%) |
| Monocarboxylic acid1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Iopamidol related compound B2 | 0.6 | 0.1 |
| Iopamidol related compound C3 and 2-chloro derivative4 | 0.9 | 0.5* |
| Iopamidol | 1.0 | — |
| 2,3-Dihydroxypropyl isomer5 | 1.1 | 0.1 |
| Diiodo derivative6 | 1.2 | 0.1 |
| Acetyl analog7 | 1.3 | 0.1 |
| Hydroxyethyl derivative8 | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| O-Acetyl iopamidol9 | 2.2 | 0.1 |
| N,N-Dimethylamino derivative10 | 2.3 | 0.1 |
|
*
These peaks, appearing at a relative retention time of 0.9, are integrated together to determine conformance.
1
3-(1,3-Dihydroxypropan-2-ylcarbamoyl)-5-(S)-lactamido-2,4,6-triiodobenzoic acid.
2
5-Glycolamido-N1,N3-bis(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propyl)-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide.
3
4-Chloro-N1,N3-bis(1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-yl)-5-(S)-lactamido-2,6-diiodoisophthalamide.
4
2-Chloro-N1,N3-bis(1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-yl)-5-(S)-lactamido-4,6-diiodoisophthalamide.
5
N1-(1,3-Dihydroxypropan-2-yl)-N3-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-5-(S)-lactamido-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide.
6
N1,N3-Bis(1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-yl)-5-(S)-lactamido-2,4-diiodoisophthalamide.
7
5-Acetamido-N1,N3-bis(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propyl)-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide.
8
N1-(1,3-Dihydroxypropan-2-yl)-N3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-(S)-lactamido-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide.
9
(S)-5-(2-Acetoxypropanamido)-N1,N3-bis(1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-ylcarbamoyl)-2,4,6-triiodoisophthalamide.
10
N1-(1,3-Dihydroxypropan-2-yl)-5-(S)-lactamido-2,4,6-triiodo-N3,N3-dimethylisophthalamide.
|
||
Assay—
Transfer about 300 mg of Iopamidol, accurately weighed, to a glass-stoppered, 125-mL conical flask, add 40 mL of 1.25 N sodium hydroxide and 1 g of powdered zinc, connect the flask to a reflux condenser, and reflux the mixture for 30 minutes. Cool the flask to room temperature, rinse the condenser with 20 mL of water, disconnect the flask from the condenser, and filter the mixture. Rinse the flask and the filter thoroughly, adding the rinsings to the filtrate. Add 5 mL of glacial acetic acid, and titrate with 0.1 N silver nitrate VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Each mL of 0.1 N silver nitrate is equivalent to 25.90 mg of C17H22I3N3O8.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Ian DeVeau, Ph.D.
Director, Veterinary Drugs and Radiopharmaceuticals 1-301-816-8178 |
(RMI05) Radiopharmaceuticals and Medical Imaging Agents 05 |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 2668
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 33(6) Page 1179
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.